| Modified : sep. 26th 2017 |
Dual GATED SLEW
|
 |
back to summary |
 |
 |
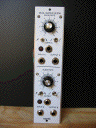
| Description |
| Modified : sep. 26th 2017 |
Dual GATED SLEW
|
 |
back to summary |
 |
 |
| Description |
|
 |
 |
Schematic |
 |
 |
 |
 |
List of parts and building instructions
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wiring |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
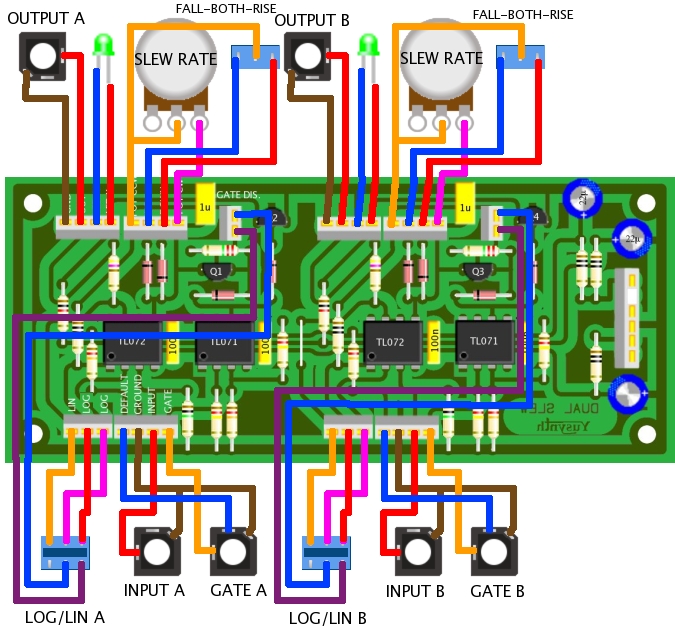 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Trimming
|
| This circuit requires
no setting
or trimming. It must work right away. |
 |
 |
References |
Information and
datasheet for BF245  Information and datasheet for BS170  |
 |
 |
  |
| Name :
Patrick Pseudo : Baronrouge Modular project: JHC live lab Location: Toulon, France Web site : http://myspace.com/patjhc |
Name : Pseudo : Julien Modular project: Location : France Web site : |
Name : Pseudo : Sebo Modular project : Location : Argentina Website : http://www.cosaquitosenglobo.com.ar |
  |
||
| Name : Zarko Modular project : Location : Gardanne, France Website : |
|
|||
 |
 |