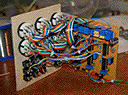
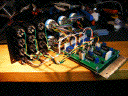
reference
|
value
|
number
|
U1,U2,U3,U4,U5,U6
|
TL074
|
6
|
R1,R2
|
10 ohm
|
2
|
R17,R18,R19,R27,R28,R29,R37,R38,R39
|
100 ohm
|
9
|
R6,R8
|
470 ohm
|
2
|
R4
|
4.7k
|
1
|
| R3 |
39k
|
1
|
| R14,R16,R24,R26,R34,R36 |
100K 0.1% (take a batch of
1% and select those within 0.1%)
|
6
|
R7
|
156K (a 180K in parallel
with a 1.2M)
|
1
|
R5,R12,R22,R32
|
180K
|
4
|
| R10,R11,R13,R20,R21,R23,R30,R31,R33 |
200K 0.1% (take a batch of
1% and select those within 0.1%) |
9
|
R15,R25,R35
|
1M
|
3
|
R9,R19,R29
|
3.3M
|
3
|
| C5,C6,C7 |
100nF |
3
|
| C1,C2 |
10µF or
22µF/35V electro. |
2
|
C3,C4
|
100µF/35V electro.
|
2
|
T11,T12,T13,T14,T14,T15,T16,T17,18,T19,T20
|
1K 10 (or 15 or 25) turn
trimmer |
10
|
T1,T2,T3,T4,T5,T6,T7,T8,T9,T10
|
10K 10 (or 15 or 25) turn
trimmer |
10
|
T21,T23,T25
|
47K 10 (or 15 or 25) turn
trimmer |
3
|
T22,T24,T26
|
220K 10 (or 15 or 25) turn
trimmer |
3
|
Jk1,Jk2,Jk3,Jk4,Jk5,Jk6,Jk7,Jk8,Jk9,Jk10,Jk11,Jk12
|
6,5 mm jack socket
|
12
|
|








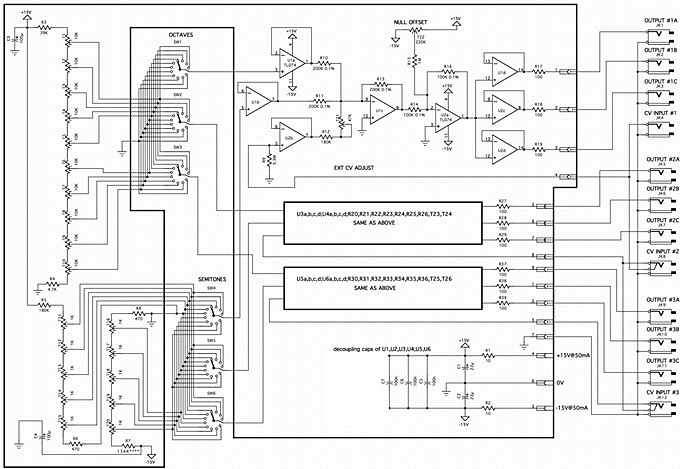


 ,
,