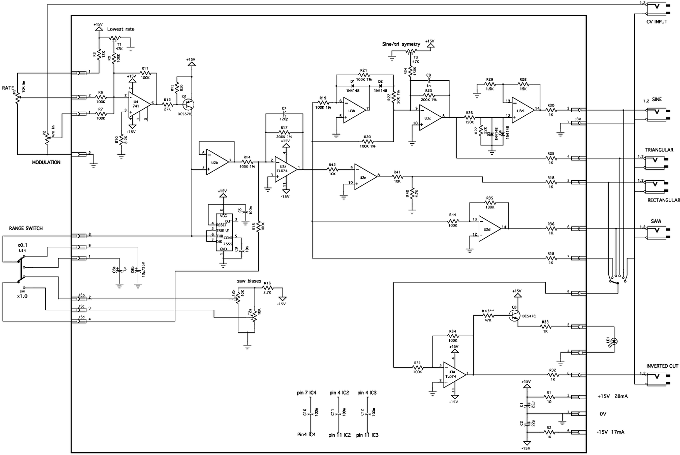
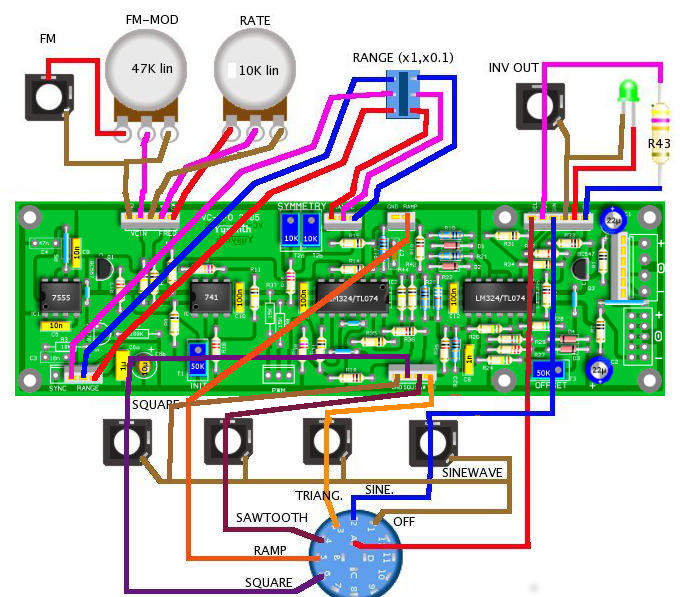
reference
|
value
|
quantity |
U1
|
7555 (CMOS
version of the 555)
|
1
|
U2,U3
|
TL074
|
2
|
U4
|
LM741 or TL071
|
1
|
Q1
|
BC557B
|
1
|
Q3
|
BC547
|
2
|
D1,D2,D3*,D4*
|
1N4148 , *
matched for better performance
|
4
|
R5
|
must be bypassed with a strap
|
|
R1,R2
|
10 |
2
|
R13
|
820 |
1
|
R18,R25,R30,R32,R33,R36
|
1K |
6
|
| R29 |
1.5K |
1
|
R16
|
2.7K |
1
|
R40
|
4.7K |
1
|
| R10 |
8.2K |
1
|
R41,R42
|
10K |
2
|
R8
|
12K |
1
|
R28
|
15K |
2
|
R27
|
22K |
1
|
R12
|
27K |
1
|
R22
|
50.1K or 49.9K |
1
|
R6,R7,R9,R11,R14,R15,R19,R20,R21,
R31,R34,R35,R44
|
100K |
13
|
R24,R26
|
150K |
2
|
R17,R23
|
200K |
2
|
C7
|
120p
|
1
|
C8
|
1n
|
1
|
C5,C9
|
10n
|
2
|
C10,C11,C12
|
100n
|
3
|
C6a
|
1u
|
1
|
C6b
|
10uF
|
1
|
C1,C2
|
22uF
|
2
|
T2a,T2b
|
10K multi-turn
|
2
|
T1,T3
|
47K or 50K
multi-turn
|
2
|
P1
|
10K lin
|
1
|
P2
|
47K lin
|
1
|
LD1
|
yellow LED
|
1
|
SW1
|
DPDT switch
|
1
|
SW2
|
rotary switch 6
pos. |
1
|
JK1..JK6
|
jack socket
|
6
|
|