| Updated : jan. 30th, 2016 | ARP VCF |
 |
back to summary |
 |
 |
| Description |
| Updated : jan. 30th, 2016 | ARP VCF |
 |
back to summary |
 |
 |
| Description |
|
 |
 |
Schematics |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Building details |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wiring |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General
wiring |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
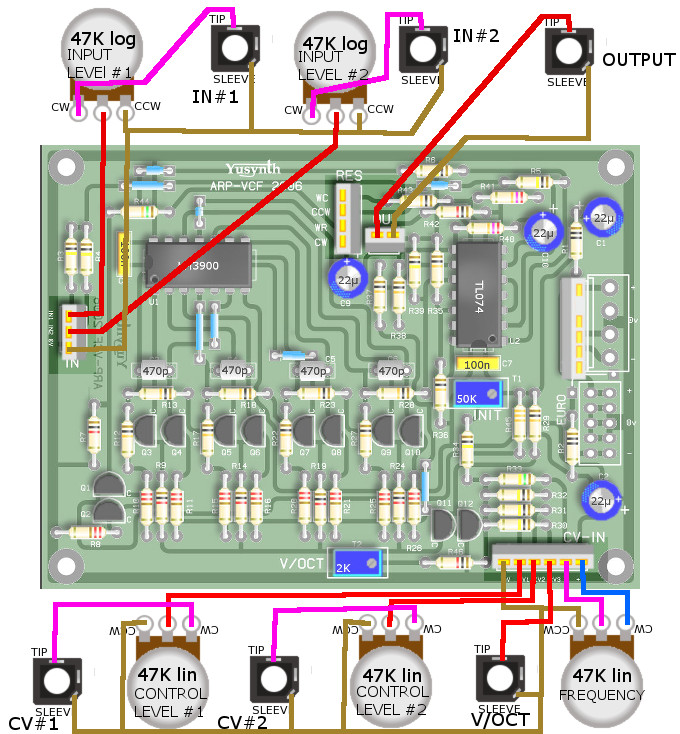 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Trimming |
V/Octave tracking :
Optional settings
|
| Thanks to Thalassa77, here is
comparison of the Yusynth ARP clone and the genuine
ARP 4075 filter. |
 |
 |
References |
| Here are
interesting links where to find schematics and infos
about the ARP VCF : |
 |
 |
 |
| Name : Gergö
PALATINSZKY Modular project : Fractal / Frakta'l Location : Budapest, Hungary Website : What a nice front panel indeed ! |
Name : Wasubot Modular project : Location : Australia Website : |
Name : Czaba ZVEKAN
Modular project : Location : Basel, Switzerland Website : |
 |
 |
 |
| Name
: Pseudo : Etaoin Modular project : Casia MS01 Location : Utrecht, Netherlands Website : www.casia.org/modular |
Name
: Suit and Tie Guy Pseudo : Modular project : STG-Soundlab Location : Chillicothe, USA Website :www.suitandtieguy.com |
Name
: Pseudo : Funky40 Modular project : Location : Switzerland Website : |
 |
  |
|
| Name
: Patrick Pseudo : Baronrouge Modular project: JHC live lab Location: Toulon, France Web site : http://myspace.com/patjhc |
Name
: Frederic Monti Pseudo : Zarko Modular project: Location: Gardanne, France Web site : |
|
|||
 |
 |